什麼是心房纖顫?
視頻: 【香港大學醫學院 - 心房顫動心臟健康專題 - 剪輯撮要】 簡易家用心房顫動測試
認識心房纖顫
心房纖顫是什麼?
心房纖顫(Atrial fibrillation)是一種最常見的心律不正疾病,主要可分為偶發性、持續性及永久性。 在心房纖顫的情況下,心房 (心臟上方的腔室) 跳動每分鐘超過三百次以上,帶動心室迅速顫動或抽動, 這可能導致血液積聚在心臟的心房中,並形成血塊。 這些血塊可以隨着血液進入腦部,導致中風。
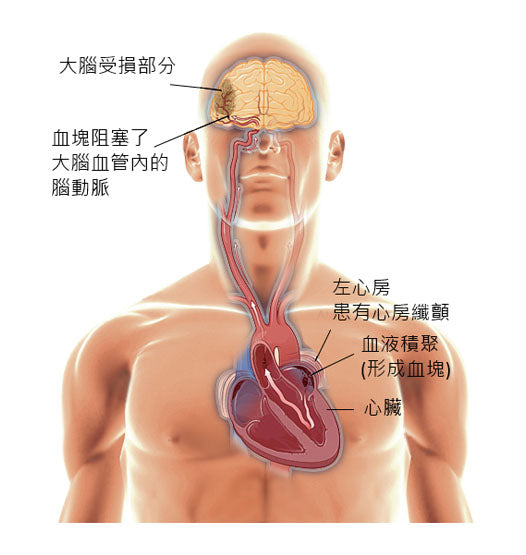
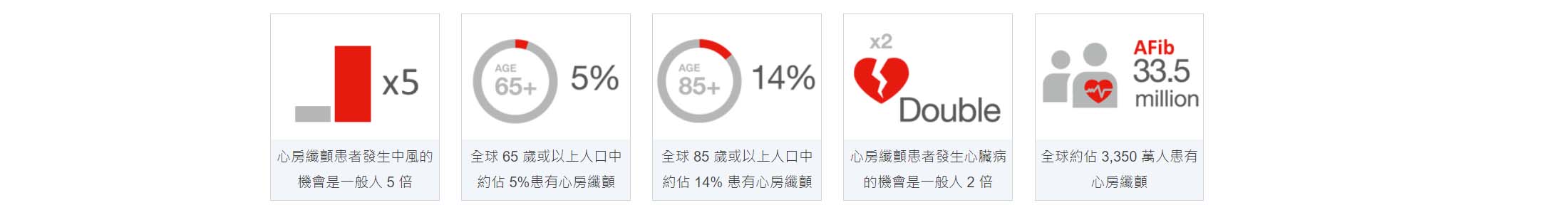
心房纖顫引起中風的機會較一般高[1]。 心房纖顫患者發生中風的機會是一般人的5倍[6-8]。大約40%的心房纖顫患者並沒有明顯症狀[2],不少患者是由於其他原因[3],包括中風[4, 5],在送往醫院治療時才被診斷自己患有心房纖顫。
心房纖顫如同沉默的殺手,大約70%的心房纖顫患者,在病發前是沒有症狀,並且沒有被診斷出來。心房纖顫出現的初期,一般只會不規律地出現,因此患者在求診的時候,醫生也無法察覺到此病症。
心房纖顫的症狀
許多心房纖顫的患者,都沒有明顯的症狀,而可能出現的特徵和症狀,包括:[6]
- 心悸、心跳加速、不舒服和不規則心跳
- 虛弱
- 呼吸困難
- 疲勞
- 頭暈
- 思想混亂
心房纖顫的成因?
心房纖顫是最常見的持續性心律失常,引起心房纖顫的原因很多,至今對它的成因尚未完全了解。 但是,以下的危險因素都可能增加患上心房纖顫的風險:
- 年齡
- 高血壓
- 糖尿病
- 肥胖
- 冠狀動脈疾病
- 壓力
- 吸煙、過量酒精...等
那些人士較易患上心房纖顫?
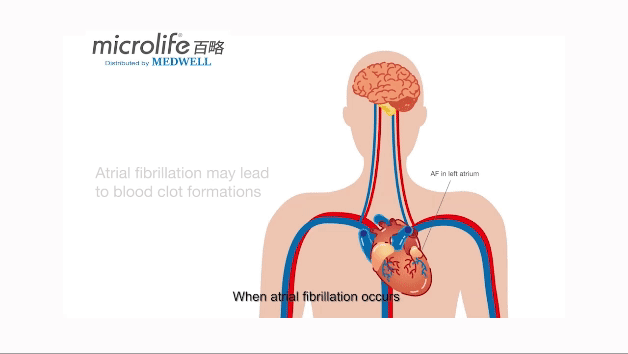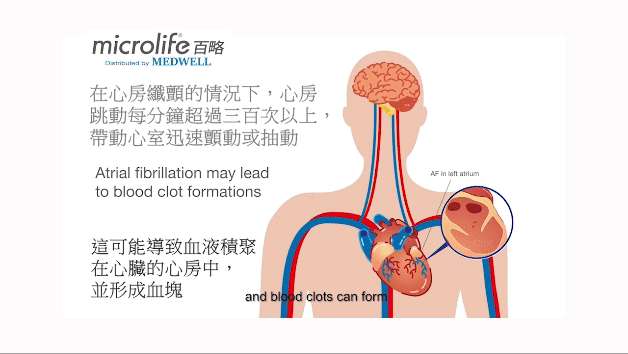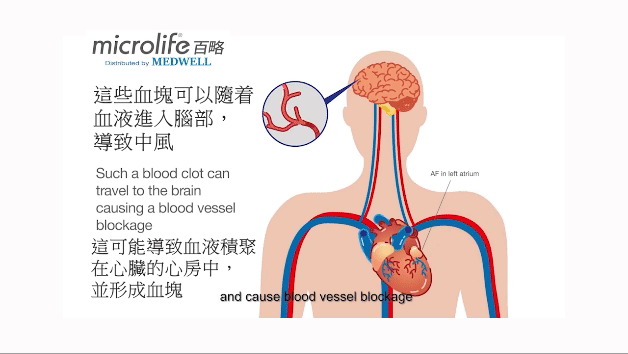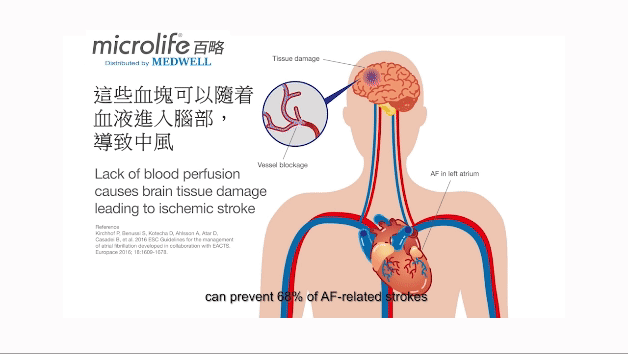
全球65歲或以上的人口中約佔5%患有心房纖顫,而85歲或以上的則佔14%。心房纖顫患者發生中風的機會是一般人的5倍,並佔所有中風個案中的20%。 由於許多患者沒有心房纖顫的症狀,因此大部份患者仍然未被確診。早期發現心房纖顫,並進行適當的治療,可以有效將中風風險降低68%。[7-9]
AFIB心房纖顫偵測血壓計
-
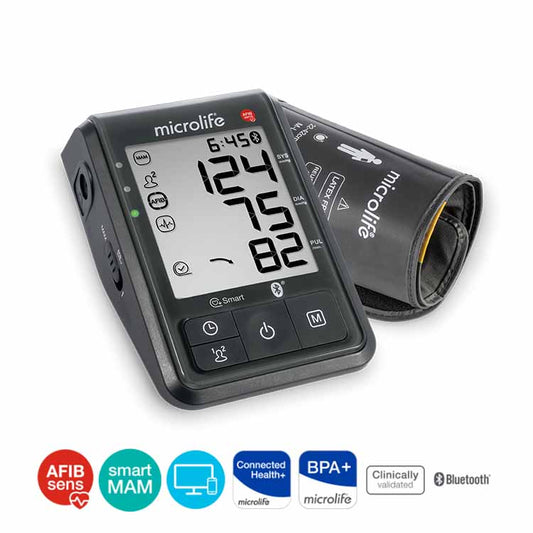
百略microlife BP B6 ADVANCED CONNECT 藍牙全自動血壓計, 檢測心房纖顫
定價 HK$1,480.00定價單價 / 每 -
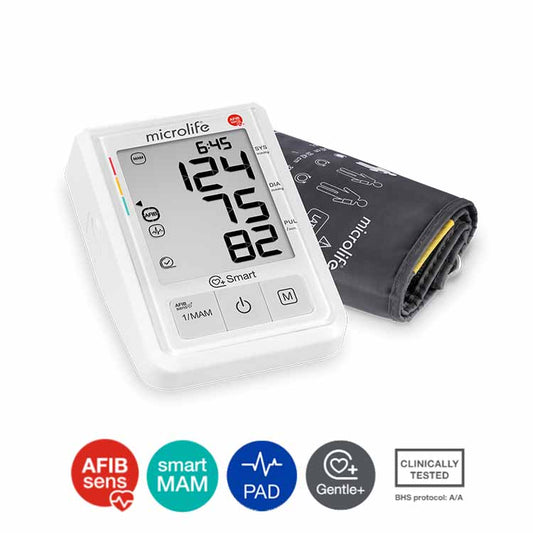
百略microlife BP B3 AFIB 全自動手臂式血壓計,檢測心房纖顫
定價 HK$1,380.00定價單價 / 每