Video:Microlife Patented AFIB Technology
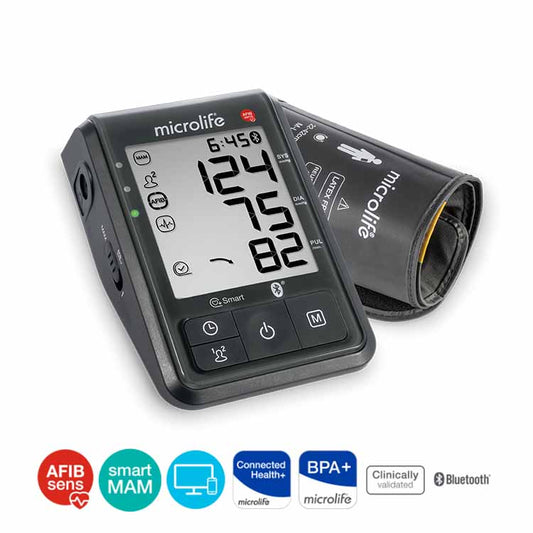
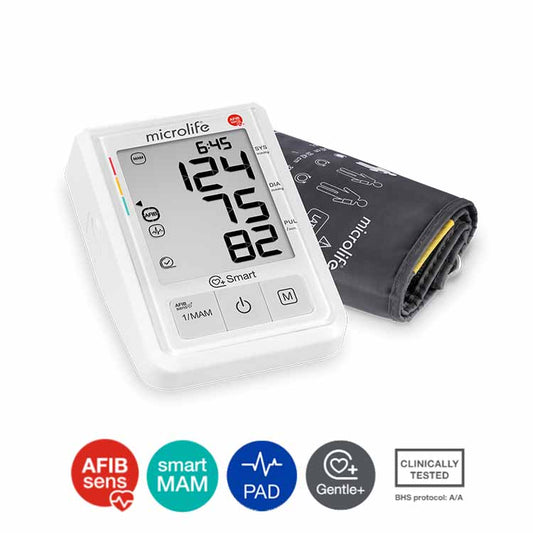
Microlife AFIB Technology
-

The most reliable atrial fibrillation (AFIB) check for measuring blood pressure at home
PATENTED AFIB TECHNOLOGY
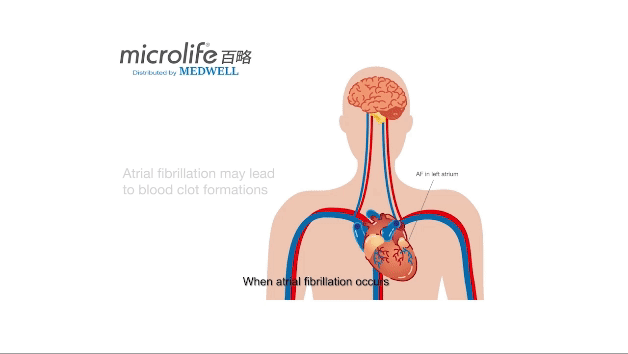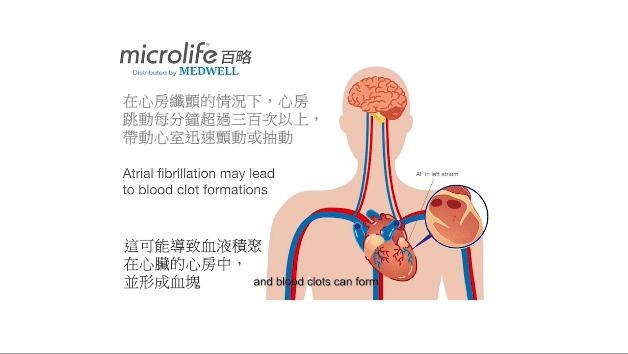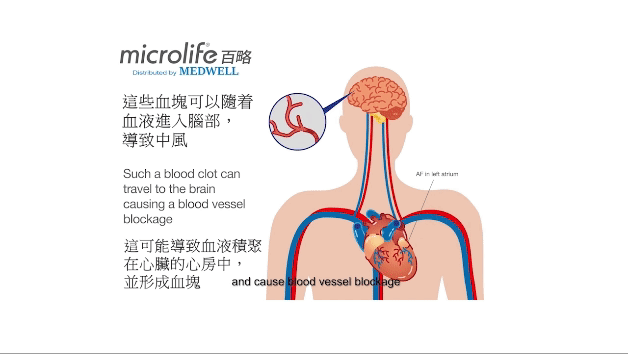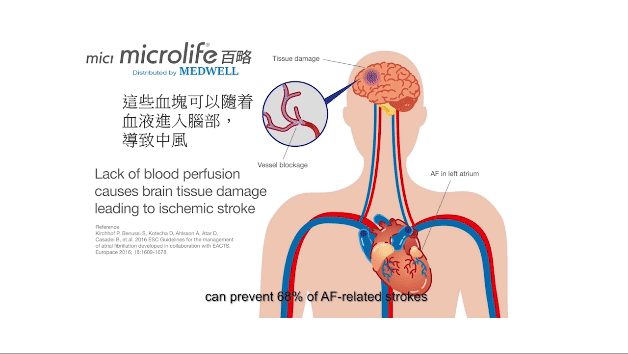
Atrial fibrillation (AFIB) is one of the most common heart rhythm disorders. It is often asymptomatic and difficult to diagnose, but it is an important cause of stroke. Microlife AFIB is the world's only, medically proven technology for blood pressure devices that detects dangerous Atrial fibrillation (AFib). The high degree of accuracy has been proven several times in clinical trials and has been recommended by international specialists and physicians.
HOW AFIB TECHNOLOGY WORKS?
The majority of the available blood pressure devices allow blood pressure measurements to be applied simultaneously to irregular heartbeats and arrhythmias. However, this does not distinguish between the different types of arrhythmias.
Microlife blood pressure monitors with implemented AFIB Technology allow patients to be screened for Atrial fibrillation during blood pressure measurements at home. An algorithm calculates the irregularity index, which is the standard deviation divided by mean based on interval times between heartbeats. If AFib is detected during blood pressure measurements, the AFIB symbol is displayed. Microlife AFIB does not make a diagnosis, but provides important information for your doctor, who can refer you for a 12-lead ECG to confirm the presence of AFib.
A systematic review of all clinical evidence to the Microlife AFIB detector [1] showed that the highest sensitivity value (98%) is obtained when three sequential blood pressure measurements were performed with two or three AFib positive readings. The highest specificity value (89%) is obtained when with three sequential measurements, of which all three must be AFib positive. For this reason the Microlife blood pressure monitors with AFIB technology automatically measure three times.
Focus on screening for atrial fibrillation
Accurately focus on screening for atrial fibrillation. Microlife's atrial fibrillation detection is clinically proven to be highly sensitive (98%) and highly specific (92%)
-

Clinical studies have accumulated more than 10,000 samples and have been published in internationally renowned journals.
-

Clinical evidence shows that measuring blood pressure in primary care and at home, while detecting atrial fibrillation, can be used as a reliable tool for primary screening of AF.
RECOMMENDED BY NICE (UK)
Professional recommendation from doctors: No. 1 Atrial Fibrillation Detection Technology
The Microlife AFIB detection system has convincingly proven its accuracy, and showed that it leads to increased detection of new patients with AFib when used in general clinical practice. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in United Kingdom officially recommends using Microlife WatchBP Home A during routine blood pressure measurement for all general practitioners in UK. [2]
- “The available evidence suggests that the device reliably detects atrial fibrillation and may increase the rate of detection when used in primary care.”
- “WatchBP Home A should be considered for use in people with suspected hypertension and those being screened or monitored for hypertension, in primary care.”
- Prevention of 2,000 strokes per year in the UK (81 per 100,000 patients screened aged 65 - 75 years and 182 per 100,000 patients aged 75 years and older).
- Healthcare cost savings of € 31 million a year.
References:
1. Verberk WJ, Omboni S, Kollias A, Stergiou GS: Screening for atrial fibrillation with automated blood pressure measurement: Research evidence and practice recommendations. Int J Cardiol 2016; 203:465-473.
2. NICE: WatchBP Home A for opportunistically detecting atrial fibrillation during diagnosis and monitoring of hypertension http://guidance.nice.org.uk/MTG13. 2013; Assessed 18 Aug. 2015.
3. AFIB technology[EB/OL]. https://www.microlife.com/technologies/blood-pressure/afib-technology.
International clinical evidence list
Atrial fibrillation AFIB detection patented technology related products
-
MICROLIFE BP B6 CONNECT BLUETOOTH® BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR WITH STROKE RISK DETECTION
Regular price HK$1,480.00Regular priceUnit price / per -
Microlife BP B3 AFIB Blood Pressure Monitor with STROKE RISK DETECTION
Regular price HK$1,380.00Regular priceUnit price / per
2013 Oxford Trail Oxford Clinical Trial
The famous Oxford University in the UK conducted a randomized clinical trial on 1,000 home medical patients in 2013. The results showed:
Ballroom Medical's AFIB is the best choice for the preliminary screening of atrial fibrillation. It measures blood pressure at the same time. The operation is simple and does not require professional explanation, and its accuracy is comparable to the single-lead ECG used in the clinic.
"So in primary care and home use, Microlife AFIB is more suitable as a screening tool for atrial fibrillation than ECG. These data suggest using atrial fibrillation technology for home blood pressure measurement, which has excellent diagnostic accuracy, so it can be used during initial diagnosis. It can be used as a reliable screening test." - Dr. George S. Stergiou (ESH member, famous European hypertension expert, has published 5 books & more than 150 related studies)
Domestic and foreign references
-
- Nichols M TN, Luengo-Fernandez R, Leal J, Gray A, Scarborough P, Rayner M European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2012. European Heart Network, Brussels, European Society of Cardiology, Sophia Antipolis 2012.
- Boriani G, Laroche C, Diemberger I, Fantecchi E, Popescu MI, Rasmussen LH et al.: Asymptomatic atrial fibrillation: clinical correlates, management, and outcomes in the EORP-AF Pilot General Registry. Am J Med 2015; 128:509-518 e502.
- Zoni-Berisso M, Lercari F, Carazza T, Domenicucci S: Epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: European perspective. Clin Epidemiol 2014; 6:213-220.
- Sanna T, Diener HC, Passman RS, Di Lazzaro V, Bernstein RA, Morillo CA et al.: Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2014; 370:2478-2486.
- Gladstone DJ, Spring M, Dorian P, Panzov V, Thorpe KE, Hall J et al.: Atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. N Engl J Med 2014; 370:2467-2477.
- Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, Savelieva I, Atar D, Hohnloser SH et al.: 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation–developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 2012; 14:1385-1413.
- Hart RG, Benavente O, McBride R, Pearce LA: Antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 1999; 131:492-501.
- Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, Hoffman EB, Deenadayalu N, Ezekowitz MD et al.: Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014; 383:955-962.
- Verberk WJ, Omboni S, Kollias A, Stergiou GS: Screening for atrial fibrillation with automated blood pressure measurement: Research evidence and practice recommendations. Int J Cardiol 2016; 203:465-473.
- Wiesel J, Wiesel D, Suri R, Messineo FC: The use of a modified sphygmomanometer to detect atrial fibrillation in outpatients. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2004; 27:639-643.
-
- Wiesel J, Wiesel D, Suri R, Messineo FC: The use of a modified sphygmomanometer to detect atrial fibrillation in outpatients. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2004; 27:639-643.
- Stergiou GS, Karpettas N, Protogerou A, Nasothimiou EG, Kyriakidis M: Diagnostic accuracy of a home blood pressure monitor to detect atrial fibrillation. J Hum Hypertens 2009; 23:654-658.
- Wiesel J, Fitzig L, Herschman Y, Messineo FC: Detection of atrial fibrillation using a modified microlife blood pressure monitor. Am J Hypertens 2009; 22:848-852.
- Wiesel J, Abraham S, Messineo FC: Screening for asymptomatic atrial fibrillation while monitoring the blood pressure at home: trial of regular versus irregular pulse for prevention of stroke (TRIPPS 2.0). Am J Cardiol 2013; 111:1598-1601.
- Kearley K, Selwood M, Van den Bruel A, Thompson M, Mant D, Hobbs FR et al.: Triage tests for identifying atrial fibrillation in primary care: a diagnostic accuracy study comparing single-lead ECG and modified BP monitors. BMJ Open 2014; 4:e004565.
- Wiesel J, Arbesfeld B, Schechter D: Comparison of the Microlife blood pressure monitor with the Omron blood pressure monitor for detecting atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 2014; 114:1046-1048.
- Gandolfo C, Balestrino M, Bruno C, Finocchi C, Reale N: Validation of a simple method for atrial fibrillation screening in patients with stroke. Neurol Sci 2015; 36:1675-1678.
- Chan PH, Wong CK, Pun L, Wong YF, Wong MM, Chu DW et al.: Head-to-Head Comparison of the AliveCor Heart Monitor and Microlife WatchBP Office AFIB for Atrial Fibrillation Screening in a Primary Care Setting. Circulation 2017; 135:110-112.
- Chan PH, Wong CK, Pun L, Wong YF, Wong MM, Chu DW et al.: Diagnostic performance of an automatic blood pressure measurement device, Microlife WatchBP Home A, for atrial fibrillation screening in a real-world primary care setting. BMJ Open 2017; 7:e013685.
- Alpert BS, Quinn D, Gallick D: Oscillometric blood pressure: a review for clinicians. J Am Soc Hypertens 2014; 8:930-938.
- NICE: WatchBP Home A for opportunistically detecting atrial fibrillation during diagnosis and monitoring of hypertension http://guidance.nice.org.uk/MTG13. 2013; Assessed 18 Aug. 2015.






